|
IPSDK 4.1.1.1
IPSDK : Image Processing Software Development Kit
|
| image = | darkHysteresisThreshold2dImg (inImg,highSeedThreshold,highPropagationThreshold) |
| image = | lightHysteresisThreshold2dImg (inImg,lowSeedThreshold,lowPropagationThreshold) |
| image = | hysteresisThreshold2dImg (inImg,lowSeedThreshold,highSeedThreshold,lowPropagationThreshold,highPropagationThreshold) |
Apply hysteresis thresholding to an image.
Hysteresis threshold algorithm applies two thresholds 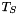 and
and 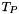 on the output image.
on the output image. 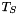 is the most restrictive threshold and yields a seed image
is the most restrictive threshold and yields a seed image  , used to propagate the marked features in
, used to propagate the marked features in 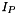 , obtained by thresholding the input image by
, obtained by thresholding the input image by 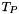 . This algorithm is commonly used in edge detection such as Canny edge detector.
. This algorithm is commonly used in edge detection such as Canny edge detector.
The aim of this threshold is to preserve the features in 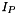 containing a seed in
containing a seed in  .
.
The algorithm needs 4 thresholds: the minimum and maximum thresholds 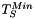 and
and 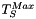 to compute the seed image
to compute the seed image  and the minimum and maximum thresholds
and the minimum and maximum thresholds 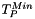 and
and  to compute the image
to compute the image 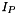 , used for the propagation.
, used for the propagation.
![\begin{eqnarray*} I_S[i] & = & \begin{cases} 1, & \text{if } T_S^{Min} \leq InImg[i] \leq T_S^{Max} \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \\ I_P[i] & = & \begin{cases} 1, & \text{if } T_P^{Min} \leq InImg[i] \leq T_P^{Max} \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} \end{eqnarray*}](form_208.png)
To simplify the algorithm parametrization, several wrappers are defined to apply this threshold:
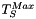 and
and  ,
, 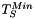 and
and 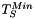 being automatically set to the image buffer type minimum value. This allows to select dark features using darker seeds on light background.
being automatically set to the image buffer type minimum value. This allows to select dark features using darker seeds on light background.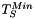 and
and 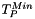 ,
, 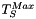 and
and 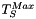 being automatically set to the image buffer type maximum value. This allows to select light features using lighter seeds on dark background.
being automatically set to the image buffer type maximum value. This allows to select light features using lighter seeds on dark background.
![\[ \left\{ \begin{array}{ccc} T_S^{Min} & \leq & T_S^{Max} \\ T_P^{Min} & \leq & T_P^{Max} \\ T_S^{Max} & \leq & T_P^{Max} \end{array} \right. \]](form_209.png)
Here is an example of dark and light hysteresis threshold applied to a gray scale input image. The intensities of each area are indicated we used 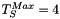 and
and  for the dark threshold and
for the dark threshold and 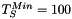 and
and 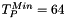 fot the light threshold:
fot the light threshold:
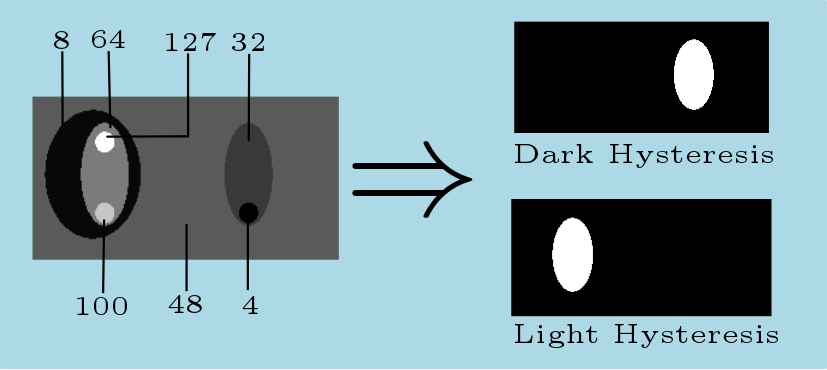
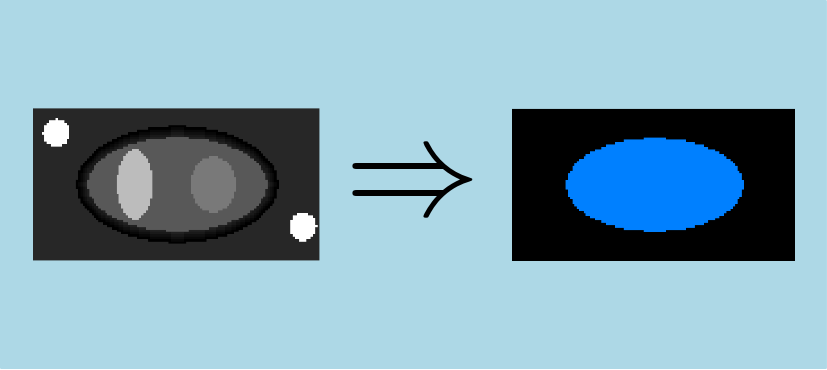
The features and seeds intensities may be higher than the minimum image intensity and lower than the maximum image intensity. The hysteresisThreshold2dImg wrapper allows to handle this case, illustrated by the following figure. In this example, the background have an intensity of 50, the two little white circles have an intensity of 255, the intensity of the central main ellipse equals 96 and the two lighter ellipses inside have an intensity of 192 (left) and 128 (right). Finally, the intensity of the contour of the main ellipse varies from 12 to 44. The threshold used for the calculation are:  ,
, 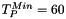 and
and 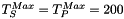 .
.